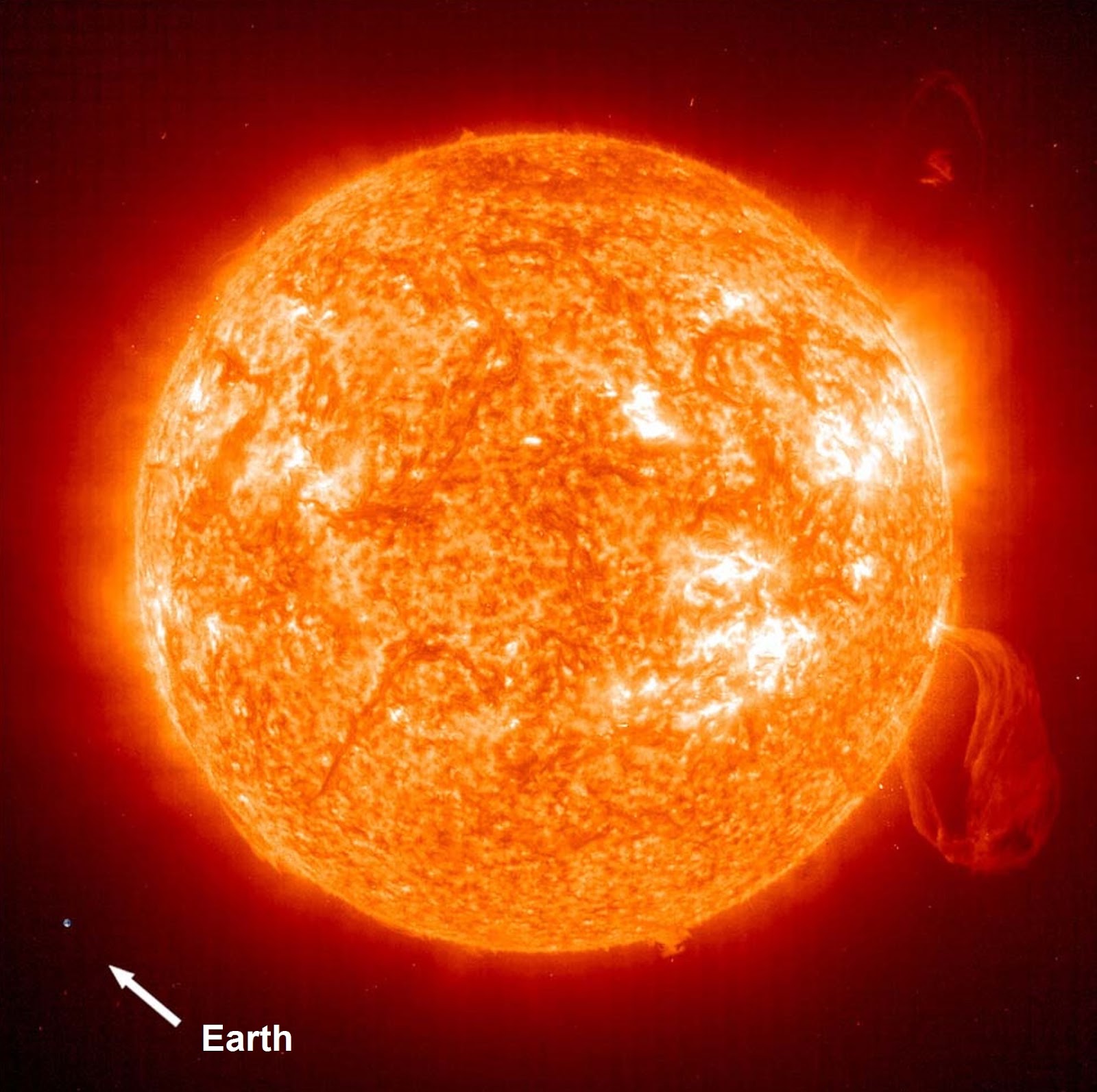
The Sun, a blazing ball of gas at the center of our solar system, dwarfs Earth in both size and mass. To put it into perspective, the Sun’s diameter is approximately 109 times that of Earth, and its volume could fit over 1.3 million Earths. This staggering difference in size highlights just how dominant the Sun is in our cosmic neighborhood. But how does this size comparison impact life on Earth and the dynamics of the solar system? The Sun's immense size isn’t just a random fact; it plays a critical role in sustaining life on Earth. Its gravitational pull keeps all the planets, including Earth, in orbit, while its energy drives weather patterns, seasons, and even photosynthesis. Understanding how big is the sun compared to earth helps us appreciate the delicate balance that allows life to thrive. Beyond its sheer size, the Sun’s mass accounts for about 99.86% of the total mass of the solar system, making it the undisputed heavyweight champion. In this article, we’ll delve deeper into the size comparison between the Sun and Earth, exploring fascinating facts, answering common questions, and uncovering why this comparison matters. From visualizing the scale to understanding the science behind it, we’ll break down complex ideas into digestible insights. By the end, you’ll not only know how big is the sun compared to earth but also gain a newfound appreciation for the star that powers our world.
Table of Contents
- How Big is the Sun Compared to Earth?
- Why is the Sun So Much Bigger Than Earth?
- What Would Happen if Earth Were as Big as the Sun?
- How Do Scientists Measure the Sun's Size?
- Can We Visualize the Sun's Size in Everyday Terms?
- What Are the Implications of the Sun's Size?
- How Does the Sun's Size Affect the Solar System?
- Frequently Asked Questions About the Sun and Earth
How Big is the Sun Compared to Earth?
When it comes to size, the Sun is nothing short of colossal. With a diameter of about 1.39 million kilometers (864,000 miles), the Sun towers over Earth, whose diameter is roughly 12,742 kilometers (7,918 miles). To better understand this, imagine Earth as a small marble. In comparison, the Sun would be a massive sphere about the size of a basketball court. This size difference isn’t just about numbers—it has profound implications for the solar system’s structure and dynamics.
But how does this size translate into volume? The Sun’s volume is so immense that you could fit approximately 1.3 million Earths inside it. To visualize this, picture filling a massive sphere with tiny marbles. Even if you had a million marbles, you’d still need hundreds of thousands more to fill the Sun’s equivalent space. This comparison underscores just how vast the Sun is compared to our home planet. Its mass is equally impressive, accounting for nearly 99.86% of the total mass of the solar system.
Read also:What Is 720p A Comprehensive Guide To Hd Resolution
Why is this comparison important? The Sun’s size and mass are directly responsible for its gravitational pull, which keeps all the planets, including Earth, in orbit. Without the Sun’s immense size, the delicate balance of the solar system would collapse. Additionally, the Sun’s size allows it to generate the energy needed to sustain life on Earth. Its nuclear fusion reactions produce light and heat, which travel millions of kilometers to reach our planet. Understanding how big is the sun compared to earth helps us grasp the Sun’s role in shaping our solar system and supporting life as we know it.
Why is the Sun So Much Bigger Than Earth?
Have you ever wondered why the Sun is so much bigger than Earth? The answer lies in the processes that formed our solar system billions of years ago. The Sun formed from a massive cloud of gas and dust, known as a solar nebula, which collapsed under its own gravity. As the nebula contracted, most of its mass accumulated at the center, forming the Sun. Meanwhile, the remaining material coalesced into planets, moons, and other celestial bodies, including Earth.
What Makes the Sun’s Formation Unique?
The Sun’s formation was a process of gravitational dominance. The central region of the solar nebula, where the Sun formed, contained the majority of the material. This concentration of mass allowed the Sun to grow to its enormous size. In contrast, Earth and other planets formed from the leftover material, which was far less abundant. This difference in available material explains why the Sun is so much larger than Earth.
How Does the Sun’s Composition Contribute to Its Size?
Another factor is the Sun’s composition. The Sun is primarily made up of hydrogen and helium, the two lightest elements in the universe. These elements are highly abundant and allow the Sun to maintain its massive size without collapsing under its own gravity. In contrast, Earth is composed of heavier elements like iron, oxygen, and silicon, which make it denser but much smaller in size. This difference in composition further highlights the disparity between the Sun and Earth.
Finally, the Sun’s size is crucial for its role as a star. Its immense mass allows it to sustain nuclear fusion, a process that generates the energy needed to power the solar system. Without its size, the Sun wouldn’t be able to produce the light and heat that make life on Earth possible. This makes the Sun’s size not just a matter of scale but a fundamental aspect of its function in the universe.
What Would Happen if Earth Were as Big as the Sun?
Imagine a world where Earth was as big as the Sun. While it might sound like the premise of a science fiction novel, such a scenario would have catastrophic consequences for life as we know it. For starters, Earth’s gravity would increase exponentially, making it impossible for humans, animals, and even plants to survive. The immense gravitational pull would crush everything on the surface, turning our planet into an uninhabitable wasteland.
Read also:Dave Isaac Motors Your Ultimate Guide To Quality Vehicles And Services
Would Earth Become a Star?
If Earth were as big as the Sun, it might even undergo nuclear fusion, transforming into a star. However, this would require Earth to accumulate enough hydrogen and helium, the primary fuels for fusion. Without these elements, Earth would simply become a massive, lifeless rock. This hypothetical scenario underscores the delicate balance that allows Earth to exist as a habitable planet.
How Would the Solar System Be Affected?
The solar system would also be thrown into chaos. Earth’s increased size and gravity would disrupt the orbits of other planets, potentially causing collisions or ejections from the solar system. The Moon, currently Earth’s faithful companion, would likely be torn apart by the planet’s gravitational pull. This domino effect would unravel the stability of the entire solar system, highlighting the importance of Earth’s current size and position.
In essence, Earth’s relatively small size is what makes it uniquely suited for life. Its size allows for a stable atmosphere, moderate gravity, and a safe distance from the Sun. These factors work together to create the perfect conditions for life to thrive. While imagining Earth as big as the Sun is an interesting thought experiment, it serves as a reminder of how special our planet truly is.
How Do Scientists Measure the Sun's Size?
Measuring the Sun’s size is no small feat, given its immense distance from Earth. Scientists use a combination of techniques to determine its diameter, volume, and mass with remarkable accuracy. One of the most common methods involves observing the Sun’s angular diameter from Earth. By knowing the distance between Earth and the Sun (approximately 149.6 million kilometers), scientists can calculate the Sun’s actual diameter using trigonometry.
Another method involves studying the Sun’s light and heat emissions. By analyzing the Sun’s spectrum, scientists can infer its size and composition. This technique, known as spectroscopy, provides valuable insights into the Sun’s structure and behavior. Additionally, space missions like NASA’s Parker Solar Probe have brought us closer to the Sun than ever before, allowing for more precise measurements.
Why is measuring the Sun’s size important? Understanding the Sun’s dimensions helps scientists predict solar activity, such as solar flares and coronal mass ejections, which can impact Earth’s climate and technology. It also aids in studying other stars, as the Sun serves as a benchmark for stellar research. These measurements underscore the importance of knowing how big is the sun compared to earth and its role in the universe.
Can We Visualize the Sun's Size in Everyday Terms?
Visualizing the Sun’s size in everyday terms can help us grasp just how massive it is. Imagine the Sun as a basketball and Earth as a tiny peppercorn. Even this analogy doesn’t fully capture the scale, but it provides a starting point. To further illustrate, if the Sun were hollow, it could hold over a million Earths inside it. This comparison highlights the Sun’s overwhelming dominance in the solar system.
What Are Some Everyday Comparisons?
- If Earth were the size of a tennis ball, the Sun would be as large as a school bus.
- The Sun’s diameter is equivalent to about 109 Earths lined up side by side.
- Its surface area is so vast that it could cover 11,990 Earths.
Why Is This Visualization Important?
Visualizing the Sun’s size in relatable terms helps us appreciate its role in the universe. It also fosters a deeper understanding of how big is the sun compared to earth and why this comparison matters. By using everyday objects and scenarios, we can bridge the gap between abstract numbers and tangible reality.
What Are the Implications of the Sun's Size?
The Sun’s size has far-reaching implications for the solar system and beyond. Its immense mass creates a gravitational pull that keeps all the planets in orbit, ensuring the stability of the solar system. This gravitational influence also extends to smaller objects, such as asteroids and comets, shaping their trajectories and preventing chaos.
Additionally, the Sun’s size allows it to generate the energy needed to sustain life on Earth. Its nuclear fusion reactions produce light and heat, which drive weather patterns, seasons, and biological processes. Without the Sun’s size and energy output, life as we know it would cease to exist.
On a cosmic scale, the Sun’s size serves as a reference point for studying other stars. By understanding the Sun, scientists can make inferences about the properties and behaviors of stars throughout the universe. This makes the Sun not just a local phenomenon but a key to unlocking the mysteries of the cosmos.
How Does the Sun's Size Affect the Solar System?
The Sun’s size plays a pivotal role in shaping the solar system. Its gravitational pull dictates the orbits of planets, moons, and other celestial bodies, maintaining the delicate balance that allows life to thrive. This gravitational dominance also influences the distribution of matter in the solar system, from the asteroid belt to the Kuiper Belt.
Furthermore, the Sun’s size determines its energy output, which affects the habitability of planets. Earth’s position in the “Goldilocks Zone” is a direct result of the Sun’s size and energy production. This zone, where conditions are just right for liquid water to exist, is a testament to the Sun’s role in supporting life.
Finally, the Sun’s size impacts its lifespan. Larger stars burn through their fuel more quickly, while smaller stars last longer. The Sun’s size places it in a sweet spot, allowing it to shine for billions of years. This longevity is crucial for the evolution of life on Earth and the stability of the solar system.
Frequently Asked Questions About the Sun and Earth
How Many Earths Can Fit Inside the Sun?
Approximately 1.3 million Earths could fit inside the Sun. This staggering number highlights the vast difference in size between the two celestial bodies.
Why Does the Sun Appear Small in the Sky?
Despite its immense size, the Sun appears small in the sky because of its distance from Earth. At an average distance of 149.6 million kilometers, the Sun’s light takes about 8 minutes to reach us, making it appear as a small, bright disc.
Will the Sun Always Be This Big?
No, the Sun is gradually expanding as it ages. In about 5 billion years, it will enter the red giant phase, growing large enough to engulf the inner planets, including Earth. This natural process is part of the Sun’s lifecycle.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding how big is the sun compared to earth reveals the Sun’s critical role in our solar system. Its immense size and mass sustain life on Earth, shape the dynamics of the solar system, and serve as a benchmark for studying other stars. By exploring